This page details how to install nagrestonf on Redhat 6 or Centos 6.
Packages that nagrestconf depends on, such as Nagios and Apache, will be installed automatically.
The instructions on this page are for installing nagrestconf and its requirements on a new server,
It is not recommended to follow these instructions on an existing server that is currently being used. It might break other applications on the server since packages might be upgraded.
Installation consists of the following steps:
Get the RPM packages for Centos/Redhat 6 from the download page then copy them to the server.
Open a terminal window or ssh session then add the EPEL repository to satisfy dependencies later on.
sudo rpm -ivh https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-6.noarch.rpm
Open a terminal window or ssh session then install nagrestconf and all plugins:
sudo yum --nogpg install nagrestconf-1.174.4-1.noarch.rpm \
nagrestconf-services-tab-plugin-1.174.4-1.noarch.rpm \
nagrestconf-services-bulktools-plugin-1.174.4-1.noarch.rpm \
nagrestconf-hosts-bulktools-plugin-1.174.4-1.noarch.rpm \
nagrestconf-backup-plugin-1.174.4-1.noarch.rpm
Ensure selinux is disabled, instructions here.
Use the two helper scripts 'nagrestconf_install' and 'slc_configure'.
sudo nagrestconf_install -a sudo slc_configure --folder=local
Create a password for nagiosadmin - for GUI access to nagios.
sudo htpasswd -bc /etc/nagios/htpasswd.users nagiosadmin a_password
Create a password for nagrestconfadmin - for GUI access to nagrestconf.
sudo htpasswd -bc /etc/nagios/nagrestconf.users nagrestconfadmin a_password
Note that, by default, the nagrestconf GUI can only be reached from the host it was installed on, localhost. To enable connecting to nagrestconf from other hosts edit the apache configuration.
For example,
Edit /etc/httpd/conf.d/nagios.conf:
sudo cp /etc/httpd/conf.d/nagios.conf /tmp
sudo sed -i 's#AuthUserFile .*#AuthUserFile /etc/nagios/htpasswd.users#i' \
/etc/httpd/conf.d/nagios.conf
Edit /etc/httpd/conf.d/nagrestconf.conf:
sudo cp /etc/httpd/conf.d/nagrestconf.conf /tmp
sudo sed -i 's#AuthUserFile .*#AuthUserFile /etc/nagios/nagrestconf.users#i' \
/etc/httpd/conf.d/nagrestconf.conf
sudo sed -i 's/allow from 127.0.0.1/allow from all/i' \
/etc/httpd/conf.d/nagrestconf.conf
sudo sed -i 's/#Require/Require/i' /etc/httpd/conf.d/nagrestconf.conf
sudo sed -i 's/#Auth/Auth/i' /etc/httpd/conf.d/nagrestconf.conf
Restart apache
sudo service httpd restart
The nagrestsconf and nagios web interfaces should be accessible now.
Log into nagrestconf with user 'nagrestconfadmin', and the password that was set above.
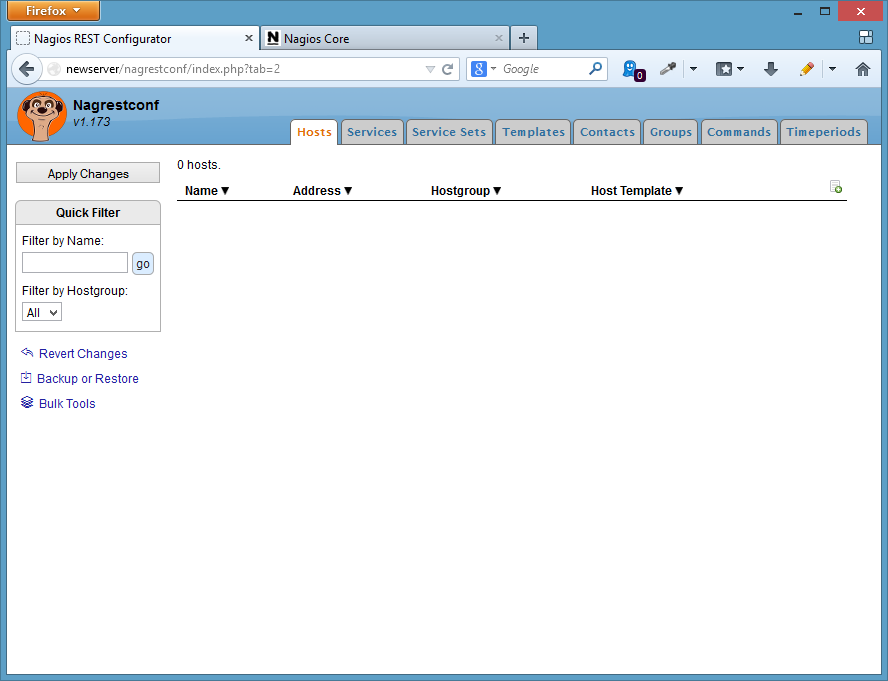
The nagrestconf interface, at 'http://server/nagrestconf', will look like the following screen shot.

Log into nagios with user 'nagiosadmin', and the password that was set above.
The nagios interface, at 'http://server/nagios', will look like the following screen shot.

To create a simple test configuration use a script that makes REST calls, or use the 'Backup/Restore' button in the nagrestconf GUI. The latter method will be used in this guide.
An example configuration can be downloaded from this link, then log into nagrestconf and use the 'Backup/Restore' button.
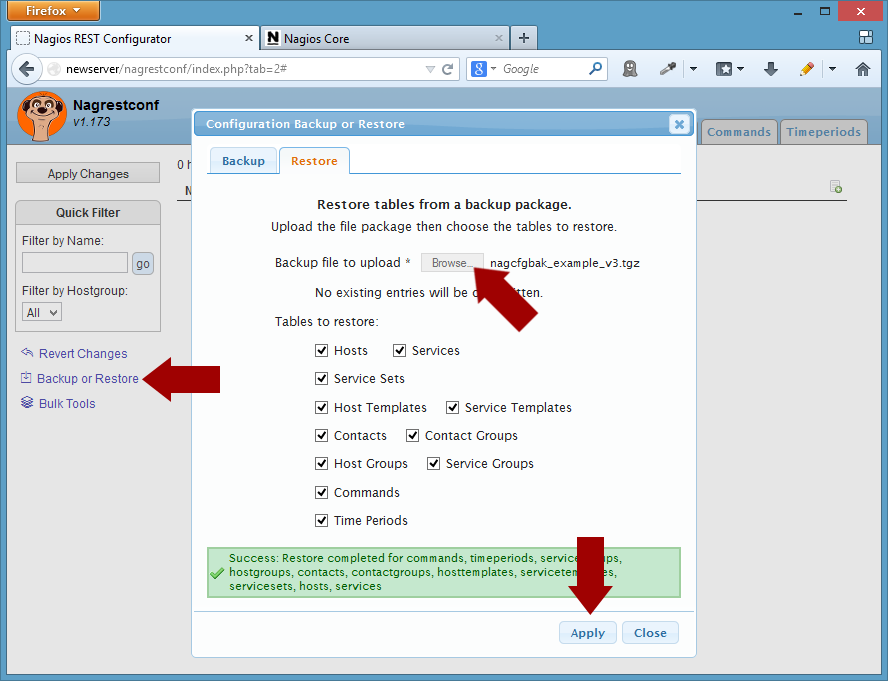


Click 'Close' in the 'Backup/Restore' dialog then refresh the page.
The new configuration will not appear in the Nagios Web interface until the 'Apply Changes' button is clicked, and then applied.
Nagios and Nagrestconf should be installed and working, however, the plugins are probably not installed so Nagios will show errors trying to run the host and service checks.
Install the plugins your distribution provides.
Choose the required plugins or install them all as below.
sudo yum install nagios-plugins-all nagios-plugins-nrpe
That's it!
comments powered by Disqus